Leeham News and Analysis
There's more to real news than a news release.
Pontifications: COTS and the KC-46A Aircraft Production Systems
Part 1 in a Boeing series about the USAF refueling tanker
By the Leeham News Team
January 17, 2022, © Leeham News: COTS is an acronym meaning Commercial Off the Shelf. It’s often a requirement for certain types of aircraft to be used by the US Air Force.
The title is a bit misleading in that in most cases, there is no directly usable off-the-shelf product, but instead, a jumping-off point that saves a tremendous amount of development. In aircraft procurement, many things have been bought this way. The advantage to the Air Force is that they get a known flyable aircraft that is for the most part debugged and has an operational history that allows the Air Force to estimate the maintenance burden and training requirements. It shaves years off the acquisition process and can be a very cost-effective way to gain new capabilities.
Pontifications: Teaming with Lockheed Martin for the KC-Y tanker competition
Jan. 10, 2022, © Leeham News: Sean O’Keefe retired from EADS/Airbus in 2014. Boeing won the re-bid contract for the US Air Force aerial refueling tanker in 2011. The third round of the tanker competitions was every bit as bitter as the second round, which Northrop Grumman/EADS won.
Boeing is in the process of producing 179 KC-46A tankers, with about half delivered. Beset by delays, technical issues, and cost overruns, Boeing nevertheless has the presumed advantage of being the incumbent supplier.
Lockheed Martin/Airbus will offer the A330-200-based MRTT tanker. Most have Rolls-Royce engines. The remainder has GE Aviation power plants. The LMXT, as the new tanker version is currently called, will be assembled in the US. If RR engines are chosen, these, too, will be assembled in the US, Lockheed says.
Although O’Keefe is no longer associated with Airbus and he is not a consultant to or otherwise advising Lockheed and Airbus, LNA asked him what he would advise if asked after benefitting from the Round 3 competition.
Airbus critics reach low blow in forthcoming KC-Y competition
By Scott Hamilton
Analysis
Jan. 4, 2022, © Leeham News: The US Air Force KC-Y tanker competition hasn’t even started but Boeing partisans already have the knives out.
For at least the fourth time, an OpEd appeared attacking Airbus for illegal subsidies. For good measure, the writer also pointed to Airbus’ misdeeds in its bribery scandal and other misadventures. All this in what increasingly appears to be the opening shots in a campaign to politicize the coming KC-Y Bridge Tanker procurement.
Once more, Boeing will be pitted against Airbus and the KC-46A against the A330 MRTT. This time, Airbus partnered with Lockheed Martin to take on Boeing. The latest column hit the Internet on Christmas Eve. This time, a Congressional staffer called on Airbus to be “Grounded” in the KC-Y competition.
This column was one of the most irresponsible commentaries seen so far. And this is saying something.
Pontifications: Assessing the advantages Boeing, Lockheed Martin-Airbus have in KC-Y tanker competition
Fourth in a Series
Jan. 3, 2022, © Leeham News: As the US Air Forces gears up to solicit bids for its KC-Y aerial refueling “bridge tanker” competition, Boeing is now the incumbent tanker supplier.
Having won the KC-X competition against Airbus, Boeing is supplying a total of 179 tankers based on the 767-200ER. The KC-46A, however, has been plagued with problems, delays, and cost overruns.
As the incumbent, Boeing would seem to have an advantage in the KC-Y competition. But on the other hand, the problems that Boeing has had in technical compliance categories, failures, and delivery delays, and foreign object debris issues, could work against it.
Sean O’Keefe was the president of EADS North America, Airbus’ parent when Boeing won the KC-X contract. He also worked for the government as the NASA administrator and on The Hill. He was friends with Bob Gates, the Secretary of Defense during parts of the Bush 43 and Obama administrations. This gives him a special insight from government and industry perspectives to weigh the advantages and disadvantages Boeing faces in the anticipated KC-Y contest that will likely pit the incumbent against the Lockheed Martin-Airbus team that will once again offer the A330-200-based tanker called the LMXT.
Pontifications: Applying commercial production principles to the A330 MRTT
Second in a series.
Dec. 13, 2021, © Leeham News: When EADS, the forerunner of Airbus Group, pondered whether to proceed on its own to compete with the A330 MRTT for the US Air Force’s aerial tanker competition, the factors went well beyond the tanker.
Plans for the Airbus A320 program, production ramp-up, and potentially a US final assembly line also were weighed.
“An assessment was made as a consequence of having been through the competition once before and learning from that,” said Sean O’Keefe. O’Keefe was CEO of EADS North America at the time.
Then, O’Keefe said in an interview with LNA in October, was the realization of what Airbus was doing to really ramp up production on A320s. Airbus had a plethora of things to figure out what that would take.
Pontifications: Retrospective of KC-X tanker competition
The first in a series.
By Scott Hamilton
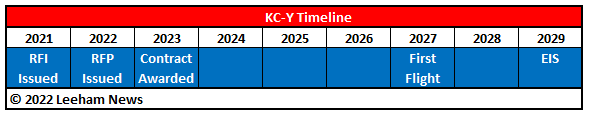
Dec. 6, 2021, © Leeham News: The US Air Force began the process this year to procure the KC-Y aerial refueling tanker.
Originally, this was to follow the KC-X (awarded to Boeing in the form of the KC-46A) to replace the McDonnell Douglas KC-10. This has been altered to be a bridge tanker between the KC-X and the KC-Z, an advanced tanker design that is in the conceptual stage.
The KC-Y promises to be a contest between Boeing, for more KC-46 orders, and a partnership between Lockheed Martin and Airbus based on the A330-200 MRTT. MRTT stands for Multi-Role Tanker Transport. The Lockheed Martin plane is called the LMXT, for now.
The KC-X competition was bitter and repetitive. A partnership between Northrop Grumman and Airbus initially won the contract. But Boeing protested how the USAF scored the bake-off. The General Accounting Office upheld the protest. A new competition saw the contract awarded to Boeing.
KC-Y is only in the Request for Information stage and neither Boeing nor Lockheed have submitted filings yet. But already, the surrogate Boeing campaign appears underway.
Pontifications: Biden’s new “Buy American” policy may hit Lockheed Martin-Airbus plans to compete in KC-Y tanker bid
Aug. 2, 2021, © Leeham News: A move by the Biden Administration may have unintended consequences in the KC-Y Bridge Tanker procurement by the US Air Force.
The Bridge Tanker is the Air Force’s second round to replace the aging Boeing KC-135 fleet. Between 140-160 airplanes will be purchased under KC-Y. The Air Force awarded a contract to Boeing in the previous KC-X procurement for 179 tankers based on the 767-200ER platform.
President Joe Biden announced last week that the US will adopt a rule under its Buy American policy that American content must be increased from 55% to 60% immediately and ultimately 75%.
If adopted, the rule appears to all but preclude an expected proposal by a partnership between Lockheed Martin and Airbus (LMA) to offer the KC-330 Multi-Role Tanker Transport (MRTT). This is based on the A330-200 platform.
Lockheed Martin did not respond to a request for comment.
HOTR: USAF prepares for new tanker competition, pitting Lockheed Martin/Airbus and Boeing against each other
By the Leeham News Team
June 22, 2021, © Leeham News: The US Air Force appears to be preparing a new round of competition for the next phase of its aerial refueling tanker recapitalization.
The first, KC-X, took more than 10 years to award a contract that didn’t get overturned. Boeing initially was awarded a lease deal in 2001 that was canceled in the wake of a scandal that sent two Boeing officers to jail and led to the resignation of CEO Phil Condit.
Round two pitted Boeing against Northrop Grumman and EADS, which was the name of the parent of Airbus’ commercial unit. Northrop won, but this award was overturned when USAF improprieties were revealed in the debriefing.
Round three pitted Boeing against EADS alone after Northrop bowed out. Boeing won this contract with a price 10% below EADS, which didn’t contest the decision. Boeing since has written off about $5bn on the KC-46A tanker, which still doesn’t work as required and which was delivered nearly two years late.
Related stories:
Union asks Congress to intervene in Boeing inspection issue
Subscription Required
By Bryan Corliss
April 15, 2019, © Leeham News: As Boeing faces federal investigations, shareholder lawsuits, Congressional hearings – and possibly subpoenas – linked to the 737 MAX crashes, another issue flying low on the radar could further complicate the company’s relationship with the Federal Aviation Administration and the elected officials who oversee it.
The issue revolves around the company’s plan to end quality control inspections for several thousand tasks performed by Boeing mechanics in the factory.
That plan – first reported by The Seattle Times in January – involves the use of more “smart tools” to perform work more precisely so that inspections will no longer be required for thousands of tasks. Instead of doing quality checks 100% of the time, as Boeing inspectors have been doing for generations, inspectors will sample 1-in-100 tasks, or maybe less, Boeing executives told the newspaper.
Now, the union for inspectors whose work is going away is asking its influential supporters in Congress to intervene with the FAA. It wants a chance to show the agency data it says proves that the new process will lead to more downstream rework on the assembly line, more injured workers and more production delays.
Summary
- Borrowing from the auto business
- Union says bad decisions put deliveries at risk
- Boeing says new system brings down defects
Read more
Pontifications: I don’t know what to make of this
April 1, 2019, © Leeham News: One can’t help but think, a lot, about the two Boeing 737 MAX crashes and the facts that Boeing created the system, linked it to one sensor, not two, didn’t tell the airlines pilots about it, didn’t include it in pilot manuals, didn’t have a safety alert system as standard equipment, initially blamed the Lion Air pilots and reportedly lobbied Donald Trump not to ground the airplanes.
But my thoughts haven’t stopped here.